4 ROI formulas to help you get a raise

Know your LTV from your YOY? How about your COGS from your conversion rate? If you don’t understand anything, it’s time to review a few marketing ROI formulas. Knowing some basic ROI formulas will help you better understand the impact of your marketing campaigns and how to improve them.
Then when your boss says, “We gave you $50,000 for Facebook ads – what is the return on investment [ROI]?” or “What is our average website traffic growth rate this quarter?” you will have all the answers.
Use these four ROI formulas to analyze and prove the impact of your social media and digital marketing channels. And be sure to try our free and easy-to-use calculator to see how your efforts pay off.
What does ROI mean?
In general, ROI means return on investment. However, from a marketing perspective, ROI means the return on investment from your marketing activities and costs.
ROI is a measure of all value-creating marketing activities divided by your investment in those activities. Your ROI shows which marketing activities bring the most value.
After taking into account the time, money and resources involved, what is the measurable return for your business? To find this answer, you need to do some simple calculations to determine which marketing campaigns have generated the most value for your business.
Here is the basic ROI formula for marketing campaigns:
Marketing ROI = (Value Achieved – Investment Made) / Investment Made X 100
When your ROI is above 0, your marketing investment is making money for your business. We need a positive ROI! A negative ROI means that you invested more than you earned – in other words, you lost money.
Marketing ROI may seem daunting at first, but once you learn a few simple formulas, you can immediately tell if you’ve reached your ROI goals.
Marketers used to shy away from ROI calculations, but things are changing now. Over 80% of respondents to the Hootsuite 2022 Social Trends survey said they were confident in quantifying social media ROI. This is a big jump from 68% in 2021.
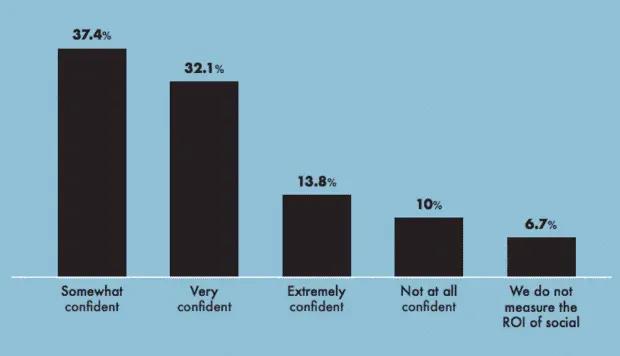
Check out the Hootsuite Social Trends Report for the full picture, or watch this short video on the state of social media ROI:
How to Measure Marketing ROI: 4 Marketing ROI Formulas
How you calculate your marketing ROI depends on your campaign goals.
It can be:
- Increasing brand awareness
- Increasing Engagement YoY
- Conversion boost
- Customer Lifecycle Extension (LTV)
Each of these goals will affect which ROI formula you use in your calculations.
Here are four marketing ROI formulas to help you get started.
Marketing ROI Formula #1: How to Measure Basic ROI
Calculating ROI is surprisingly simple. But it’s easy to fall into the common trap of using gross profit without taking into account cost of goods sold.
Here is an example of a simple ROI calculation:
- Let’s say we’re an online fashion store. We spend $100 on Instagram Story ads and sell ten T-shirts for $25 each.
- Our income from these sales is $250 (10 shirts x $25).
- We will now subtract marketing expenses ($100) from gross sales ($250). After accounting for this Instagram Story ad, we have $150.
- We then divide this number by our marketing investment ($100). Now we have 1.5.
- We multiply 1.5 by 100 to find the ROI, which is 150.
ROI = (Total Revenue – Marketing Investment / Marketing Investment) x 100
According to this baseline calculation, our ROI will be 150%, an impressive return. But, unfortunately, it’s too good to be true.
Of course, this is an easy way to calculate your ROI. But those t-shirts weren’t free so this answer is still incomplete.
You also need to consider how much it costs to produce what you’re selling and subtract that cost from your gross income. It is recommended that you calculate your marketing ROI based on the gross margin of the product or service, not the gross revenue.
Here is a more accurate way to calculate ROI.
To accurately measure ROI, you need to know the second calculation: cost of goods sold. This number will include all the costs of producing your products.
If you are selling a $25 T-shirt and only make $10 in profit from each unit, you need to include this information in your ROI calculation.
ROI = ((total revenue – total cost – marketing investment) / marketing investment) x100
Total Revenue: Sales generated from your marketing campaign (such as product purchases).
Total COGS: Cost of Goods Sold. For example, if we sell T-shirts, the cost price will include raw materials, labor, and factory costs. (You may not need to calculate this—your finance team will most likely have all the cost data they need.)
- First, calculate the cost of goods sold (COGS) and add it to the ROI equation above. Let’s say in our example, the finance department told us earlier that for every $25 T-shirt we sell, we get $15 in profit. Our cost price will be $10 per unit sold.
- If we sold ten products in our Instagram Story ad campaign, our total cost for that campaign would be $100.
- Now we can calculate the ROI. We sold ten products for $25 each, so our total revenue is $250. We know our total cost price is $100. The $100 we spent on Instagram Story ads is our marketing investment.
- Subtract our cost price ($100) and marketing investment ($100) from our total income ($250) and you get $50. Divide $50 by our total marketing investment of $100. This gives us 0.5. Multiply by 100 to get the percentage: 50.
- Our ROI is 50%, which means our Instagram ads are a worthy use of the company’s time, resources and money.
Pro Tip: We’ve created a free social media ROI calculator to help you calculate your ROI for a specific paid or organic marketing campaign. Just enter your numbers, click a button, and you’ll get a simple, public ROI calculation based on customer lifecycle value.
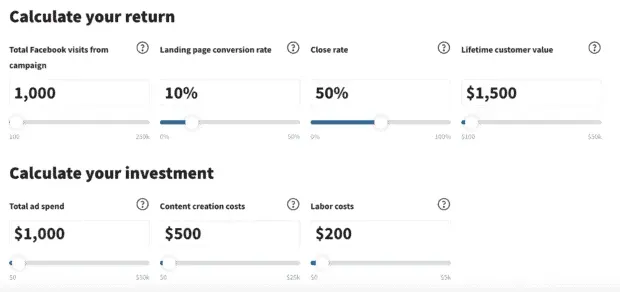
Using the numbers above, here’s what your ROI would look like:
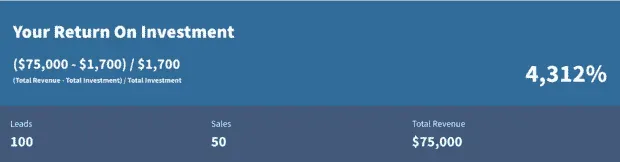
Marketing ROI Formula #2: How to Calculate Annual Growth
Our job as marketers is to drive growth and sales. And one of the best ways to showcase your results is with a year-over-year comparison (YOY).
YOY is a common method for accurately measuring growth because it helps smooth out seasonal fluctuations. For example, if you’re an e-commerce business, December’s high sales could be overshadowed by a spike in Black Friday sales. Similarly, a viral blog post one month can make the following month’s traffic stabilization look like a downturn.
But you don’t have to wait until January to use annualized calculations. YOY can help you compare months, such as how the traffic drop in July 2022 compares to your total traffic in July 2021. You can also analyze different quarters (known as quarter by quarter or QOQ).
This is a simple calculation. Select the metric you want to report on, such as total website visits from Instagram in a year.
Let’s say our total visits for 2021 was 100,000 visits, and our total visits for 2020 was 90,000 visits.
- Subtract 100,000 (current year) from 90,000 (previous year). The difference is 10000r.
- Divide 10,000 by 100,000 (current year). The answer is 0.01.
- Multiply 0.01 by 100. Answer: 10.
- Your 2021 growth rate was 10 percent, increasing social traffic from 90,000 visits in 2020 to 100,000 in 2021.
YOY Growth = ((Previous Year Total – Current Year Total) / Current Year Total) x 100
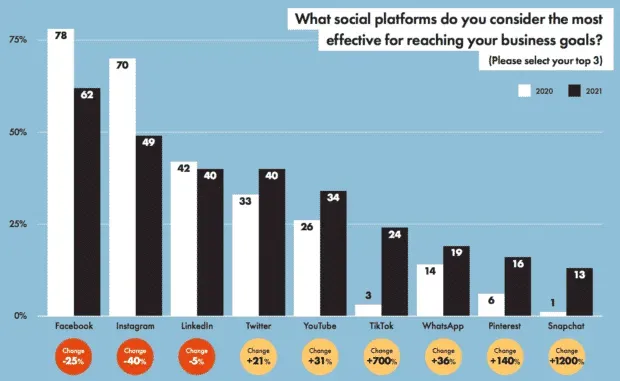
Calculating year-over-year growth regularly is also helpful for understanding which social platforms are most effective in achieving your goals.
For example, in 2020 you may have found that Facebook is the most effective in achieving your marketing goals, but in 2021 you found that TikTok and YouTube have overtaken Facebook.
In the Hootsuite 2022 Social Trends survey, marketers report that Instagram and Facebook are underperforming while TikTok and Pinterest are growing in importance. By calculating year-over-year growth, marketers can identify channels that are growing or declining in importance.
Marketing ROI Formula #3: How to Calculate Your Conversion Rate
Conversion rates are always a hot topic among marketers. People often complain about being super low when they know their campaigns are doing well. But if you have a low conversion rate, don’t worry; you are probably just wrong.
The problem is that tools like Google Analytics or Optimizely will automatically calculate the conversion rate for you. This cumulative number usually ends up in the reports.
To calculate your baseline conversion rate, follow these steps:
- First, define what a conversion is. It could be an eBook download, a newsletter signup, a product purchase, a free trial request, or any other conversion you value.
- Divide the total number of goals completed in Google Analytics by the total number of visits (this could be social media traffic, total website traffic, or total number of visits to your website).
- Multiply the answer by 100 and you’ll get your conversion rate. For example, ten newsletter subscriptions (goals achieved) divided by 1,000 website visits equals 0.1.
- To find out what it looks like as a percentage, multiply 0.01 by 100. The answer is 10, so your conversion rate is 1%.
Baseline Conversion Rate = (Total Goals Achieved / Total Visits) x 100.
“Wait, 1%?!” You think. “This can’t be!”
The problem is that you are using an aggregate number – for example, the total number of visits to your website – and not the market segments that you are actually targeting. As a result, most conversion rates appear to be low.
Himanshu Sharma, author of Math and Statistics for Web Analytics and Conversion Optimization, offers great advice for more accurate conversion rate calculations.
As he explains, “Google Analytics will take every person on the planet into account when calculating your conversion rate.”Of course, this aggregate data is not entirely useful (if your company only ships to the UK, why would you report people from Egypt who didn’t buy?).
Sharma has a simple solution: “Create and apply a new advanced segment (named ‘Target Market Traffic’) in your Google Analytics view or profile that only shows traffic from your target market.”Now you’ll see much more relevant traffic data, and your boss won’t constantly ask you why only five percent of leads convert.
To calculate a more accurate conversion rate, follow the same steps as above. This time, make sure the number you use for total hits only includes your target market by using Google’s advanced segments to filter out irrelevant traffic sources.
True Conversion Rate =
(Total number of goals achieved / total number of visits by target market) x 100
Using Google Analytics, you can also view customer touchpoints by channel, giving credit to touchpoints from when your customers first visit your site.
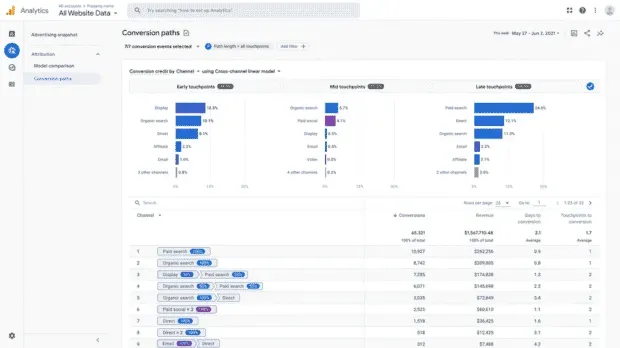
Source: Google Marketing Platform blog.
Marketing ROI Formula #4: How to Calculate Customer Lifetime Value (LTV)
Customer lifetime value measures how much a business predicts it will earn from an average customer over the life of the relationship with the business. It is a way to quantify customer relationships.
You need to know the lifetime value (LTV) of your customers in order to create accurate marketing plans.
Consider a business like Netflix. Their basic plan is $9.99. Let’s say the average user signs up and stays with them for two years before canceling. Then, after Netflix’s email marketing kicks in or they announce a new season of a show like Stranger Things, the average user re-subscribes and stays for another 15 months.
This means that the average customer brings in $389.61 for Netflix.
When advertising on Facebook or providing discounts to bring back Netflix customers, you need to keep this LTV in mind so that the marketing costs of customer acquisition do not eat into all the profit that a customer can bring.
An easy way to calculate LTV
Depending on your business model, calculating LTV can be quite complex. So, today we will stick to a simple way to calculate LTV.
LTV requires us to provide some data and answers to four key questions. Here’s what you need:
1. Average Order Value (AOV): How much does a customer spend per visit on average? For a coffee shop, this could be the amount of latte the average customer buys. For an online shoe store, this is the average amount in the basket.
How to calculate AOV:
- The best way to gather data for AOV is to work with your finance team or accountant. Every business records taxes, so your accountant will know the total sales revenue you reported last year.
- Then talk to your analytics team and get the total number of orders for the last year.
- Divide the total revenue by the total number of orders. This gives you AOV.
If you don’t have a group of accountants, upload your sales revenue data from PayPal or Stripe (or whichever you use) and then upload the total number of sales orders from your shopping cart or payment processor. If you’re using an e-commerce platform like Shopify, they usually make it easy to find those numbers.
2. Purchase frequency (PF):
How often do customers buy from you?
If you are a coffee shop, you may see the same customers every week. But if you are a mortgage broker, you may only see the same clients a few times in your life.
How to determine the frequency of purchases:
A larger business is likely already tracking this data, but a smaller one can do some simple research. For example, a coffee shop might use a loyalty card to keep track of repeat customers. Or you can ask your data team for help.
All they have to do is divide the total number of orders by the number of unique customers. This gives you your shopping frequency. For example, you can download all transactions from PayPal and analyze them in a spreadsheet.
3. Customer Value (CV): This is the average value of a customer. This is how much money we can reasonably expect to extract from our clients’ wallets.
How to calculate customer value:
- For the calculation, you will use numbers from AOV and PF.
- Multiply your AOV number (see above) by your PF number. The answer is your average customer value.
CV = AOV x PF
4. Customer life expectancy (CAL): how long will a customer remain a customer? A brand like Honda is trying to make you a customer for life (buy a Civic in college, buy a minivan when the kids come, and drive off into the sensible sunset in your fancy Accord). Of course, this varies from business to business.
Putting It All Together: Calculating LTV
Okay, you have collected all the data for the metrics listed below:
- AOV – average order value
- PF – Purchase frequency
- Summary – value for the client
- CAL – customer life expectancy
- CLV – customer lifetime value
To calculate LTV, simply complete the formula below:
CLV = CV x CAL
Multiply your CV number by your CAL number. Boom! Now you know the average CLV of your customers.
Tip: Still unsure about your ROI? Use our social media ROI toolkit to learn the basics. It includes three main resources with a simple guide and a clear framework.
Tools to help you track your marketing ROI
Now that you know the formula for calculating your marketing ROI, here are a few tools that will make tracking your ROI easier.
1. Excel or Google Sheets
Trying to figure everything out by hand gets boring pretty quickly. It also leaves you open to some obvious human error. When you’re trying to keep track of a lot of numbers, spreadsheet tools like Excel and Google Sheets come in handy. You can use them to calculate and track your marketing ROI in one place.
Here is an example of how you can use Excel to calculate the annual growth rate:
- Open an Excel sheet and create three columns: A, B, and C.
- Enter the number “2020”in cell A1. In cell A2, enter “2021”.
- Put the total amount of traffic, leads, or sales for 2020 in cell B1. In B2, enter the total amount of traffic, leads, or sales for 2021.
- Go to cell C2 and enter the following formula: =(B2-B1)/B1.
- You now have your annualized growth rate in column C.
Next, all you need to do is show your boss and wait for the promotion!
You can use Excel or Google Sheets to calculate all of your campaign’s ROI formulas. Calculating your ROI data regularly after each campaign will help you track your ROI over time and spot trends that are top performing.
If, like me, you are afraid of spreadsheets, you can purchase ready-made custom templates like the one below. All you have to do is enter your numbers and the spreadsheet will do the rest for you.
Image Source: Etsy
2. Impact Hootsuite
Hootsuite Impact measures social media marketing ROI across paid, own and earned social channels.
Impact syncs with your existing analytics systems so you can integrate your social data with the rest of your important business numbers. It simplifies reporting and provides simple recommendations to help you improve your social media ROI.
Watch this 3-minute video to learn more about using Hootsuite Impact:
You can even get automatic reports sent straight to your inbox so you don’t have to download them yourself.
Try Hootsuite for free. You can cancel at any time.
How to use your ROI calculations
Measuring your marketing ROI will help you understand the effectiveness of your campaigns, highlight their value to your organization, and improve your strategy over time. Here’s how best to use the ROI calculation.
Understand what works (and what doesn’t)
Measuring your marketing ROI is key to building and optimizing your social marketing strategy. It highlights what works and what doesn’t. Instead of guessing what your top-performing campaigns are, ROI gives you specific social media metrics. You can use these numbers to inform future strategic campaign decisions.
Prove the value of your work to management
Have you ever been told that marketing campaigns are just creative nonsense? Such a narrative ends with solid numbers in the form of a reliable ROI. So the next time your CEO says he wants to cut your marketing budget, you can come back to him with concrete evidence that your campaigns are delivering measurable value.
Knowing the ROI of your marketing campaigns demonstrates to management that resources, time, and budget are being spent on your marketing campaigns in the right way.
Discuss a higher budget for your team
It’s easier to justify spending on strategies that deliver more value than they’re worth. So when you have a great track record of delivering high ROI, you are more likely to convince management to allocate more budget to your campaigns.
Remember the big picture
While calculating marketing ROI is an integral part of any campaign, don’t get so hung up on ROI that you forget about your brand values.
Prioritizing campaigns just to get a few likes and comments won’t add value to your brand unless it’s relevant to your audience. It can even hurt your brand and audience relationships in the long run.
Knowing how to measure marketing ROI isn’t just about chasing numbers. Marketing can also help you improve customer service and build relationships with employees.
Leave a Reply