How: Your iPad has a hidden built-in calculator you don’t use – here’s how to unlock it
There is no iPad version of the Apple Calculator app, so you won’t find it on the home screen, in the App Library, or as a shortcut in the Control Center. But that doesn’t mean your iPad doesn’t have an official calculator.
Prior to the arrival of the first iPad in 2010, the Apple development team had an iPad calculator out of the box, but it was just a larger version of the iPhone app. Steve Jobs got wind of it and quickly abandoned it, and there wasn’t enough time to develop an iPad-optimized calculator before the iPad hit stores.
Now, more than 12 years later, Apple still doesn’t have an official calculator app for iPadOS – not even in iPadOS 16 (which finally added a Weather app). Craig Federighi, Apple’s senior vice president of software engineering, said in 2020 that this was because they wanted to create something “really great in that area”and that Apple “didn’t bother to make it great.”He hinted, “That day might come,” but there are too many great options on the App Store already.
However, your iPad does have a calculator; it’s just not an app like on the iPhone. Instead, it takes on various forms, each with its own benefits.
1. Search in the spotlight
When you pull down the home or lock screen, you bring up the Spotlight tool, also called Search. This feature is also available in the Today View on the lock screen and in the Notification Center. And if you’re using an external keyboard on your iPad, you can use the Command-Spacebar shortcut from any screen.
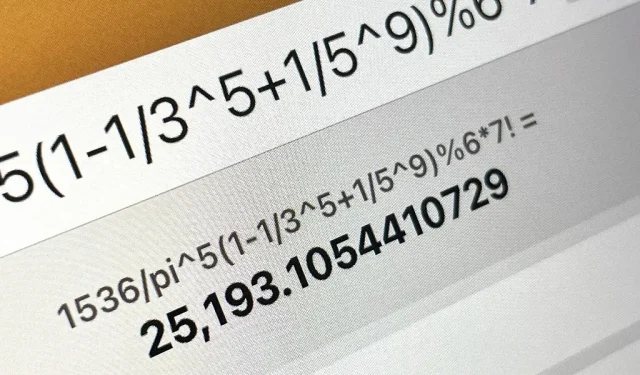
The scientific calculator is built right into Spotlight on iPadOS so you can solve math problems and get answers right away. It can perform basic arithmetic (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division) and you can use constants, trigonometric functions (sine, cosine, tangent), logarithms, roots, rounding, basic operators like exponentials and factorials, and more.
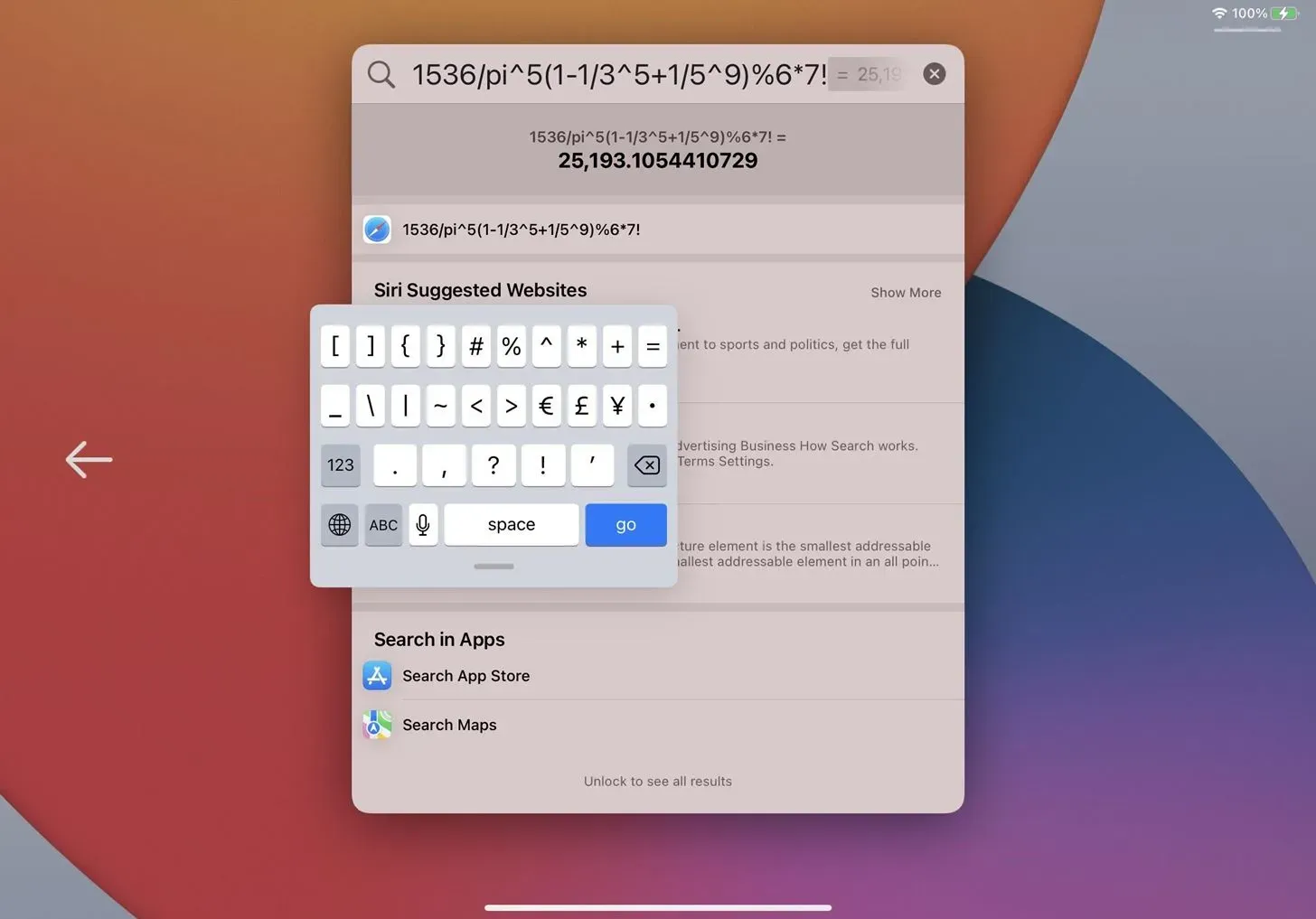
Of course, you need to type the entire problem or equation, so it’s not as convenient as a dedicated calculator app, but it gets the job done in a pinch. If you enter or paste the problem correctly, Spotlight will recognize it and offer you a solution without having to hit the equal sign (=). To copy an answer, press and hold it, then tap Copy.
Not all mathematical symbols work as a radical sign, but there are other ways to enter, as indicated below. Note that you can use some characters for different purposes, such as parentheses, percent signs, and minus signs.
Type Meaning Example Answer
----------------------------------------------------------------------
() order of operations (1+5)/2 3
% percentage 1% 0.01
- negative -6+6 0
+ addition (plus) 1+5 6
- subtraction (minus) 1-5 -4
x multiplication (times) 1x5 5
* multiplication (times) 1*5 5
() multiplication (times) 1(5) 5
/ division (divided by) 1/5 0.2
÷ division (divided by) 1÷5 0.2
pi pi pi(5) 15.7079632679
π pi π^5 306.0196847853
e Euler's number 1/e 0.3678794412
mod remainder (modulo) 7 mod 2 1
% remainder (modulo) 7%2 1
! factorial 4! 24
^ exponents (powers) 6^5 7,776
exp() natural exponent exp(2) 7.3890560989
log() base 10 logarithm log(75) 1.8750612634
ln() natural logarithm ln(75) 4.3174881135
sqrt() square root sqrt(7) 2.6457513111
cbrt() cube root cbrt(9) 2.0800838231
sin() sine in radians sin(-0.5) -0.4794255386
cos() cosine in radians cos(-0.5) 0.8775825619
tan() tangent in radians tan(-0.5) -0.5463024898
asin() inverse sine in radians asin(-0.5) -0.5235987756
acos() inverse cosine in radians acos(-0.5) 2.0943951024
atan() inverse tangent in radians atan(-0.5) -0.463647609
sinh() hyperbolic sine sinh(-0.5) -0.5210953055
cosh() hyperbolic cosine cosh(-0.5) 1.1276259652
tanh() hyperbolic tangent tanh(-0.5) -0.4621171573
asinh() inverse hyperbolic sine asinh(7) 2.6441207611
acosh() inverse hyperbolic cosine acosh(7) 2.6339157938
atanh() inverse hyperbolic tangent atanh(0.5) 0.5493061443
sind() sine in degrees sind(7) 0.1218693434
cosd() cosine in degrees cosd(7) 0.9925461516
tand() tangent in degrees tand(0.5) 0.0087268678
asind() inverse sine in degrees asind(0.5) 30
acosd() inverse cosine in degrees acosd(0.5) 60
atand() inverse tangent in degrees atand(0.5) 26.5650511771
ceil() rounds up ceil(5.6) 6
floor() rounds down floor(5.6) 5
rint() rounds to nearest integer rint(5.6) 6
fabs() absolute value fabs(-5.6) 5.6
= equality (equals)
Good to know: iPhone has a Back Tap feature that lets you access Spotlight by simply tapping the back of your iPhone two or three times. It’s much more convenient than swiping to search, but the back feature isn’t available on the iPad. However, keep reading if you need a faster way to access your iPad’s built-in calculator.
2. Siri
If you’d rather have someone else do the hard work of typing in the calculations, there’s always Siri, Apple’s built-in personal assistant. Siri can do many of the calculations listed above that Spotlight is capable of, only formulating equations is harder than typing them.
Depending on how you set up Siri, say “Hey Siri”or press and hold the Up or Home button on your iPad to get her attention. Then ask him to solve your math problem. I translated the list of Spotlight examples above into a Siri-friendly list of oral math. This is not a definitive list, but it’s a great starting point.
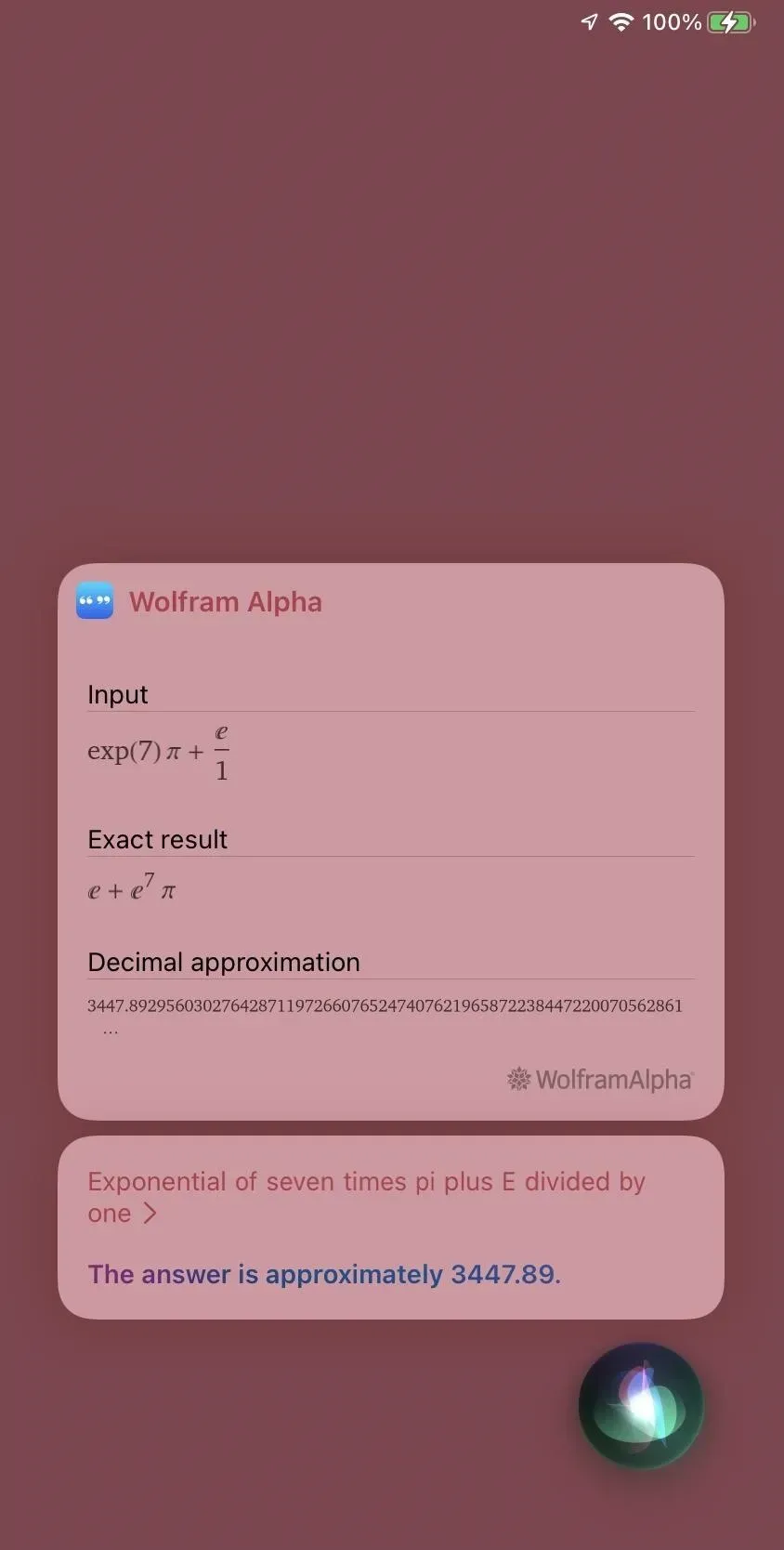
You can also type the spoken examples listed below in the Finding Answers section, but these are more than the Spotlight list above. Unlike Spotlight, Siri uses Wolfram Alpha to solve complex math problems, but Siri will use Apple’s built-in hidden calculator for simpler calculations.
Siri doesn’t always hear you correctly, so it might be wise to go to Settings -> Siri & Search -> Siri Answers and then turn on the “Always show Siri captions”toggle. If he doesn’t hear correctly, you can click on what he thinks you said and edit it using the pop-up keyboard.
Written Spoken
---------------------------------------------------------
(1+5)/2 parenthesis 1 plus 5 parenthesis divided by 2
1% 1 percent in decimal
decimal of 1 percent
-6+6 negative 6 plus 6
1+5 1 plus 5
1-5 1 minus 5
1x5 1 times 5
1 multiplied by 5
multiply 1 and 5
1 asterisk 5
1 ex 5
1*5 (same as 1x5 above)
1(5) (same as 1x5 above)
1/5 1 divided by 5
divide 1 by 5
one fifth
1 over 5
1÷5 (same as 1/5 above)
pi(5) pi times 5
pi multiplied by 5
multiply pi and 5
pi asterisk 5
pi ex 5
π^5 pi power of 5
pi to the power of 5
pi raised to the 5th power
pi caret five
1/e 1 divided by e
divide 1 by e
1 over e
7 mod 2 (nothing works correctly)
7%2 (nothing works correctly)
4! 4 exclamation mark
factorial of 4
6^5 6 power of 5
6 to the power of 5
6 raised to the 5th power
6 caret five
exp(2) exponential of 2
e to the power of 2
e raised to the 2nd power
e caret 2
log(75) common log of 75
common logarithm of 75
common log parenthesis 75 parenthesis
base 10 log of 75
base 10 logarithm of 75
ln(75) log of 75
logarithm of 75
natural logarithm of 75
natural log of 75
log parenthesis 75 parenthesis
sqrt(7) square root of 7
cbrt(9) cube root of 9
sin(-0.5) radian sine of negative. 5
radian S I N of negative. 5
radian sin of negative. 5
cos(-0.5) radian cosine of negative. 5
radian C O S of negative. 5
tan(-0.5) radian tangent of negative. 5
radian tan of negative. 5
radian T A N of negative. 5
asin(-0.5) inverse sine of negative. 5
inverse S I N of negative. 5
inverse sin of negative. 5
arc sine of negative. 5
arc S I N of negative. 5
arc sin of negative. 5
acos(-0.5) inverse cosine of negative. 5
inverse C O S of negative. 5
arc cosine of negative. 5
arc C O S of negative. 5
atan(-0.5) inverse tangent of negative. 5
inverse tan of negative. 5
inverse T A N of negative. 5
arc tangent of negative. 5
arc tan of negative. 5
arc T A N of negative. 5
sinh(-0.5) hyperbolic sine of negative. 5
hyperbolic S I N of negative. 5
hyperbolic sin of negative. 5
cosh(-0.5) hyperbolic cosine of negative. 5
hyperbolic C O S of negative. 5
tanh(-0.5) hyperbolic tangent of negative. 5
hyperbolic tan of negative. 5
hyperbolic T A N of negative. 5
asinh(7) inverse hyperbolic sine of 7
inverse hyperbolic S I N of 7
inverse hyperbolic sin of 7
acosh(7) inverse hyperbolic cosine of 7
inverse hyperbolic C O S of 7
atanh(0.5) inverse hyperbolic tangent of. 5
inverse hyperbolic tan of. 5
inverse hyperbolic T A N of. 5
sind(7) exact value of sine 7
exact sine of 7
exact S I N of 7
exact sin of 7
cosd(7) exact value of cosine 7
exact C O S of 7
tand(0.5) exact value of tangent. 5
exact tangent of. 5
exact tan of. 5
exact T A N of. 5
asind(0.5) A S I N D of parenthesis. 5 parenthesis
acosd(0.5) A C O S D of parenthesis. 5 parenthesis
atand(0.5) A T A N D of parenthesis. 5 parenthesis
ceil(5.6) ceiling function of 5.6
floor(5.6) floor function of 5.6
rint(5.6) 5.6 rounded to nearest integer
fabs(-5.6) absolute value of negative 5.6
absolute of negative 5.6
If you don’t like talking to Siri – especially in public or quiet places (classroom, library, movie theater, etc.) – turn on “Typing for Siri”in Settings -> Accessibility -> Siri -> “Enter text for Siri”. Each time you long press the Up or Home button, Siri opens the keyboard so you can type.
You can use many of the Spotlight examples in the first list with Type to Siri, but you’ll need to use the Siri examples instead if they get confusing – and this will happen from time to time.
3. Labels
While not as convenient as the first two options above, you can use Shortcuts, Apple’s scripting app, to solve some math problems and equations. The downside is that you need to create shortcuts first to do your calculations.
- Compute: Performs a numeric operation on the input and returns the result.
- Evaluate Expression: Evaluates the mathematical expression in the given input string and outputs the result as a number.
- Calculate Statistics: Calculates statistics on the numbers provided as input.
- Format File Size: Formats the file size into text.
- Number Format: Formats a number into text.
- Get numbers from input: Returns numbers from the output of the previous action.
- Number: Passes a number to the next action.
- Random Number: Passes a random number between the given minimum and maximum to the next action. The minimum and maximum numbers are included as possible results.
- Round Number: Rounds the numbers passed into the action.
If you’ve used shortcuts before, you might be able to figure out how to build your own calculator using the information above. However, you will need to use more actions than just the provided calculator actions for anything useful. A little JavaScript can help with more complex calculations.
If that sounds intimidating, some Shortcuts users have created calculators that you can download and use. None of them are perfect, but they are a good basis for figuring out how to code your own version.
- cdavid calculator (via ShortcutsGallery.com)
- Calculator by FifiTheBulldog (via RoutineHub.co)
- Calculator (iOS 13) by _qwertyuiop_ (via RoutineHub.co)
- Calculator by Roakley (via RoutineHub.co)
- Calculator by TheTechCoder100 (via RoutineHub.co)
- Calculate Tips (via Apple)
Any shortcut you create or use can be added as a widget to your Home screen or Today view (available through the Lock screen, Home screen, and Action Center). You can also ask Siri to open the shortcut up.
Leave a Reply