Pixel 7 only tests 64-bit Android and can’t run 32-bit apps

Here’s the surprise: We knew Android was preparing to drop support for 32-bit apps soon, and the upcoming Pixel Tablet would get code reviews to make it ready to run on 64-bit Android only. What no one noticed is that the Pixel 7 is also dropping support for 64-bit apps, so its release yesterday takes a big step towards Android’s 64-bit future. Esper Sr. Technical Editor Mishaal Rahman figured out all the ins and outs of how this would work.
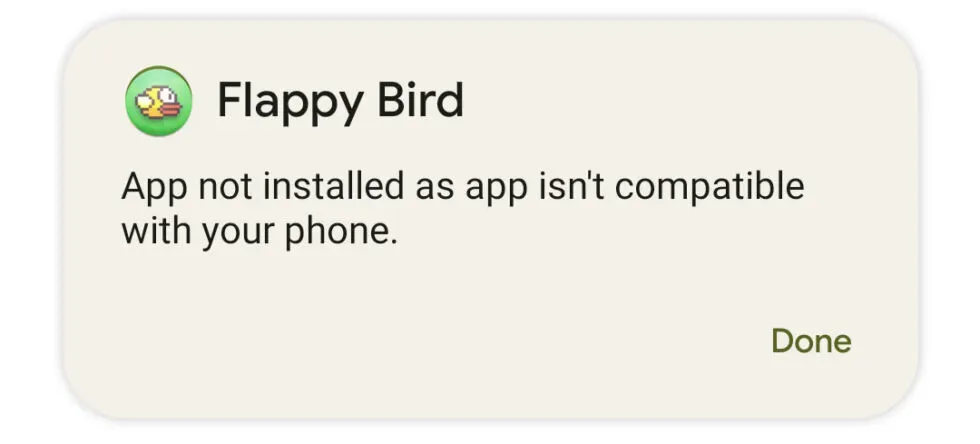
It looks like the Pixel Tablet will still be the first to run only 64-bit Android, and the Pixel 7 is only half a step closer to that milestone. Thirty-two-bit apps are disabled with a software flag, but only the 64-bit build of Android is not working yet. When trying to install a 32-bit application, an error message will appear: “The application is not installed because it is not compatible with your phone.”
It looks like the OS isn’t quite ready for 64-bit builds, as some system libraries are still 32-bit, but that’s what Google is aiming for. Also, starting with an artificial software flag is a good example. Google can see exactly how many problems 64-bit alone will cause, and can easily disable the flag in a software update if things get too bad.
However, in reality, most consumers will not notice the loss of 32-bit applications. Java apps are compiled by Android RunTime (ART) and the runtime can just produce 64-bit binaries! One problem is non-Java applications (usually games) for which the developer will need to create 64-bit builds. However, the Play Store made 64-bit support mandatory for all app updates back in 2019, so the only issues should be with abandoned apps that are a few years old. A prime example is the 2013 hit Flappy Bird.
Only 64-bit mode will soon be a reality for new Android devices. Even though Tensor 2 in the Pixel 7 still supports 32-bit per core, it’s probably the only 2022 flagship phone that can boast of it. This year’s Qualcomm and Samsung flagship SoCs only support 32-bit technologies on three of the eight cores, and Arm’s proposed X3 SoC design for 2023 does not support 32-bit technologies at all. With an eye to the Chinese market, Qualcomm is reportedly dropping support for 32-bit systems so soon and may not follow Arm’s guidelines.
Once the full 64-bit Android builds are up and running, presumably we’ll see better performance and better security by removing all that 32-bit junk. Rahman says one Google internal study showed a 5 to 10 percent improvement in performance and energy efficiency, as well as reduced RAM and storage requirements.
Leave a Reply